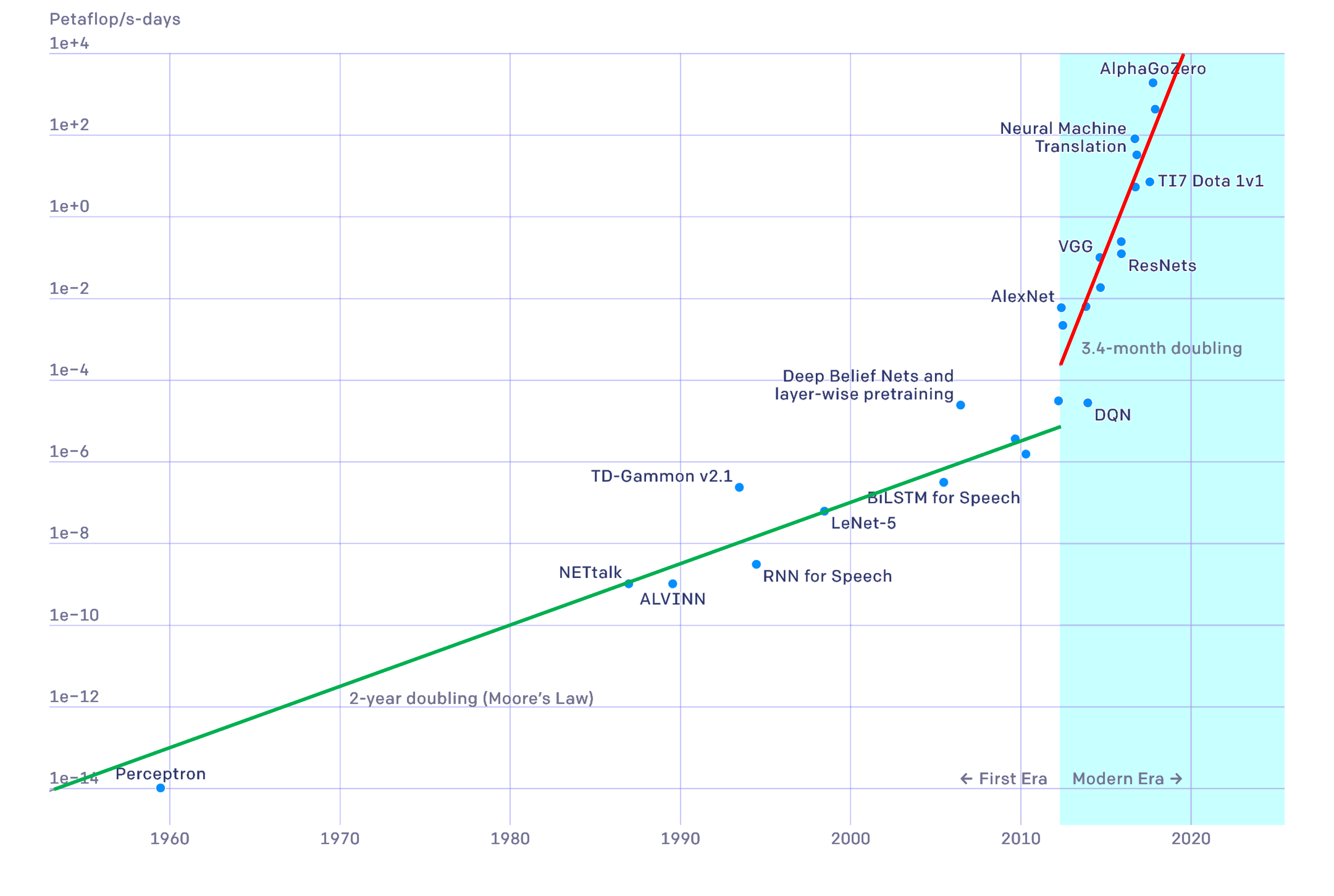
1 The Deep Learning Revolution
Machine learning (ML) today is one of the most important, and fastest growing, fields of technology. Applications of machine learning are becoming ubiquitous, and solutions learned from data are increasingly displacing traditional hand-crafted algorithms. This has not only led to improved performance for existing technologies but has opened the door to a vast range of new capabilities that would be inconceivable if new algorithms had to be designed explicitly by hand.
One particular branch of machine learning, known as deep learning (DL), has emerged as an exceptionally powerful and general-purpose framework for learning from data. Deep learning is based on computational models called neural networks which were originally inspired by mechanisms of learning and information processing in the human brain.
The field of artificial intelligence (AI), seeks to recreate the powerful capabilities of the brain in machines, using machine learning methods. Many of the AI systems in current use represent applications of machine learning which are designed to solve very specific and focused problems, and while these are extremely useful they fall far short of the tremendous breadth of capabilities of the human brain. This has led to the introduction of the term artificial general intelligence (AGI), to describe the aspiration of building machines with this much greater flexibility. After many decades of steady progress, machine learning has now entered a phase of very rapid development. Recently, massive deep learning systems called large language models (LLMs) have started to exhibit remarkable capabilities that have been described as the first indications of artificial general intelligence.
This chapter offers a general discussion to the field of deep learning, its applications, and also introduces the basic concepts and procedures of machine learning through a working example. A double introduction to the ends and the begins!
1.1 The impact of DL
1.1.1 Medical diagnosis
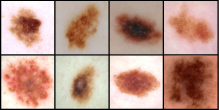
1.1.2 Protein structure

1.1.3 Image synthesis

1.1.4 LLM
1.2 A tutorial example
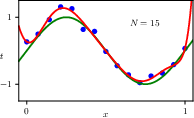
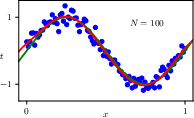
1.2.1 Synthetic data
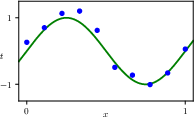
1.2.2 Linear models
1.2.3 Error function
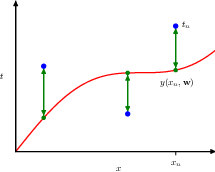
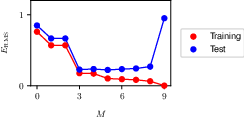
1.2.4 Model complexity
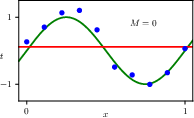
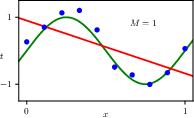
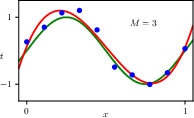
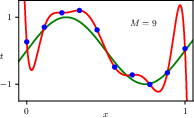
1.2.5 Regularization
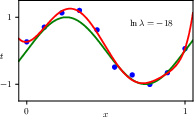
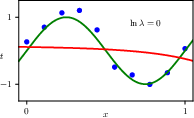
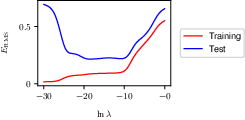
1.2.6 Model selection
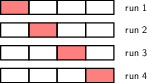
1.3 A brief history of ML
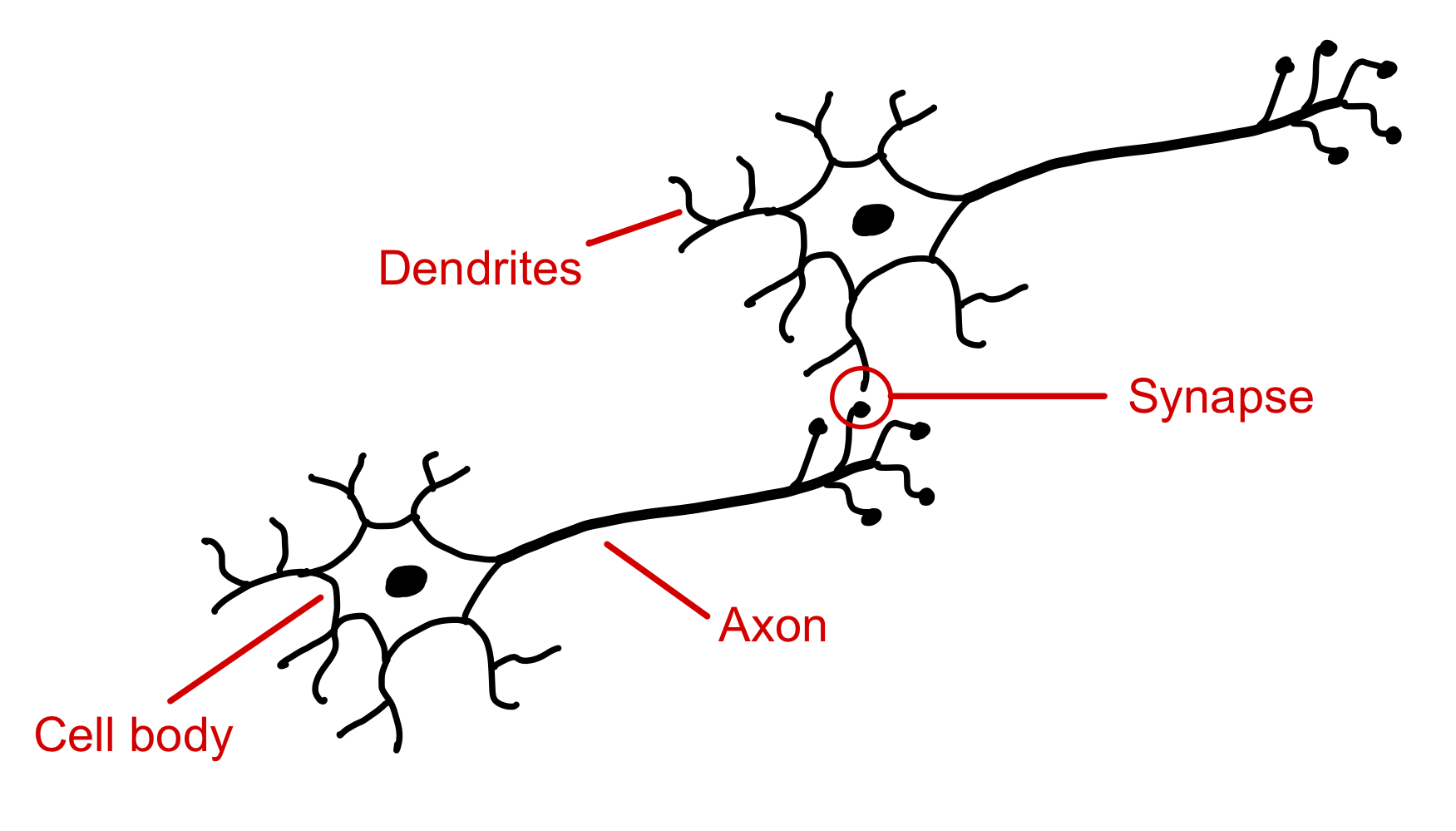
1.3.1 Single layer networks
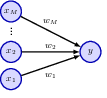
1.3.2 Backpropagation
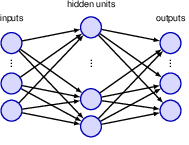
1.3.3 Deep networks